Dr. Beach’s Top 10 Beaches Of 2021
Dr. Beach’s Top 10 Beaches of 2021
For more than 30 years, Dr. Beach, aka Dr. Stephen Leatherman, has created an annual Top 10 Beach list. A professor and coastal geomorphologist at Florida International University, Dr. Beach factors in 50 different criteria including water color, sand softness, wave size, water temperature and more.
As we get ready to launch Landsat 9 this fall, we’re taking a tour of Dr. Beach’s Top 10 US beaches of 2021 as seen by Landsat 8.
10. Coast Guard Beach, Cape Cod, Massachusetts

Coast Guard Beach is located just north of the remote Nauset Inlet on Outer Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Except for the picturesque old white Coast Guard station that still sits atop the glacial bluffs, there is no development here; the best way to reach this beach is by bicycle from the Salt Pond Visitor’s Center or shuttle bus.
First mapped by Champlain in 1605, the shifting sands of this inlet are clearly visible in the Landsat image. This location is also at the point where the glacial sea cliffs transcend into a barrier beach (e.g., sand spit) that provides protection for the lagoon and development of lush salt marshes.
“In my early days as a Professor at Boston University and later at the University of Massachusetts at Amherst, I spent many summer and some winter-time days conducting scientific studies along this barrier beach.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Coast Guard Beach on May 1, 2021.
9. Beachwalker Park, Kiawah Island, South Carolina

Beachwalker Park is a public beach located on the southern part of Kiawah Island, South Carolina. This barrier island in the Charleston area is 10-miles long and features a fine grained, hard-packed beach that can be traversed easily by bicycle.
This Landsat image shows a huge accumulation of sand as a series of shoals on the south end of the island, which can be reached from Beachwalker Park. These sandy shoals will eventually coalesce, becoming an extension of the sand spit that is the south end of Kiawah Island.
“In the early 2000s, I served as the beach consultant to the Town of Kiawah Island because their world-famous golf course on the north end was being threatened by severe erosion. It was necessary to artificially bypass some sand on the north end of the island so that the normal flow of sand along the island was reinstated, saving the outermost link of this PGA golf course.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Beachwalker Park on April 9, 2021.
8. Coronado Beach, San Diego, California

Coronado Beach in San Diego is the toast of Southern California with some of the warmest and safest water on the Pacific coast. This 100-meter-wide beach is an oasis of subtropical vegetation, unique Mediterranean climate, and fine sparkling sand.
The harbor serves as a major port for the Navy’s Pacific fleet, the home port for several aircraft carriers. The docks and the crossing airplane runways for the Naval base are visible in this Landsat image.
“I really enjoy visiting this beautiful beach as well as having lunch and drinks, taking advantage of the hotel’s beachside service.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Coronado Beach on April 23, 2020.
7. Caladesi Island State Park, Dunedin Clearwater, Florida

Caladesi Island State Park is located in the small town of Dunedin on the Southwest Florida coast. The stark white undeveloped beach is composed of crystalline quartz sand which is soft and cushy at the water’s edge, inviting one to take a dip in the sparkling clear waters.
While island is still in the Park’s name, Caladesi is no longer a true island as shown on the Landsat image--it is now connected to Clearwater Beach.
“Caladesi is located in the Tampa area, but it seems like a world away on this getaway island.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Caladesi Island State Park on April 9, 2021.
6. Duke Kahanamoku Beach, Oahu, Hawaii

Duke Kahanamoku Beach is named for the famous native Hawaiian who was a big-board surfer and introduced surfing as a sport to mainland Americans and indeed the world.
One of the prominent features on this Landsat image is Diamondhead with its circular shape near the coast. This large cone of an extinct volcano provides the iconic backdrop for photos of Waikiki Beach.
“This is my favorite spot at the world-famous Waikiki Beach where you can both play in the surf and swim in the calm lagoonal waters.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Duke Kahanamoku Beach on May 17, 2020.
5. Lighthouse Beach, Buxton, Outer Banks of North Carolina

Lighthouse Beach in the village of Buxton is located at Cape Hatteras, the most northern cape in the Outer Banks of North Carolina. This lifeguarded beach is the number one surfing spot on the US Atlantic Coast as the large offshore sand banks, known as Diamond Shoals, cause wave refraction focusing wave energy on this beach.
The Landsat image shows the seaward growth of south flank of Cape Hatteras as evidenced by the parallel lines of beach ridges.
“It is fun to walk down the narrow sand spit, more exposed at low tide, as waves are approaching from both directions because of the bending of the waves.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Lighthouse Beach on May 3, 2020.
4. St. George Island State Park, Florida Panhandle

St. George Island State Park, located on the Florida panhandle and far from urban areas, is a favorite destination for beachgoers, anglers and bird watchers as nature abounds. Like other beaches on the panhandle, this long barrier island has a sugary fine, white sand beach.
In this Landsat image, St. George can be seen north of the bridge that links this barrier island to the mainland. The enclosed bay behind St. George Island is fairly shallow and the water much less clear as shown on the Landsat image, but it is not polluted.
“Besides swimming in the crystal-clear Gulf of Mexico waters, I enjoy beachcombing and shelling. While this island was hit hard in 2018 by Hurricane Michael, it has substantially recovered as there was little development to be impacted.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of St. George Island State Park on October 13, 2020.
3. Ocracoke Lifeguard Beach, Outer Banks of North Carolina

Ocracoke Lifeguarded Beach at the southern end of Cape Hatteras National Seashore was the first seashore to be incorporated into the National Park Service system.
The Landsat image shows Ocracoke to the north as separated by an inlet from Portsmouth Island. The village of Ocracoke was built at the wide area of the island where it was protected from oceanic waves during coastal storms which include both winter nor’easters and hurricanes.
“Ocracoke was once the home of the most infamous pirate Blackbeard and is still a very special place—my favorite getaway beach.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Ocracoke Lifeguard Beach on May 3, 2020.
2. Cooper’s Beach, Southampton, New York

Cooper’s Beach in the tony town of Southampton on the south shore of Long Island, New York is shielded from the cold Labrador current, making for a fairly long summer swimming season. The white quartz sand is medium to coarse grained with some pebbles, making the beach slope fairly steeply into the water.
This Landsat image shows the fairly large coastal pond named Mecox Bay to the east with Shinnecock Inlet and Bay also displayed to the west. Coopers Beach is hundreds of yards wide, made of grainy white quartz sand and is backed by large sand dunes covered by American beach grass.
“I spent several decades conducting scientific studies of this very interest oceanic shoreline because it is so dynamic and the beachfront real estate so expensive. Some of the most gorgeous and expensive residential houses in the United States are located in the world-famous Hamptons.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Coopers Beach on August 30, 2019.
1. Hapuna Beach State Park, Big Island Hawaii

Hapuna Beach State Park is a white coral sand beach that resides in a landscape dominated by dark brown lava flows on the Big Island of Hawaii. The crystal-clear water is perfect for swimming, snorkeling, and scuba diving during the summer months in contrast to winter big-wave days when pounding shorebreaks and rip currents make swimming impossible.
Hapuna and the other pocket beaches appear as an oasis in this otherwise fairly bleak landscape except for the areas irrigated as prominently shown on the Landsat imagery by the green vegetation.
“This volcanically active island is the only place that I know where you can snow ski at the high mountain tops and water ski in the warm ocean water on the same day.” – Dr. Beach
Landsat 8 collected this image of Hapuna State Park on January 5, 2021.
What’s your favorite beach?
View Dr. Beach’s 2021 picks and see Landsat views of these beaches over time.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
More Posts from Science-child and Others

Got a question about black holes? Let’s get to the bottom of these odd phenomena. Ask our black hole expert anything!
Black holes are mystifying yet terrifying cosmic phenomena. Unfortunately, people have a lot of ideas about them that are more science fiction than science. Don’t worry! Our black hole expert, Jeremy Schnittman, will be answering your your questions in an Answer Time session on Wednesday, October 2 from 3pm - 4 pm ET here on NASA’s Tumblr! Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Jeremy joined the Astrophysics Science Division at our Goddard Space Flight Center in 2010 following postdoctoral fellowships at the University of Maryland and Johns Hopkins University. His research interests include theoretical and computational modeling of black hole accretion flows, X-ray polarimetry, black hole binaries, gravitational wave sources, gravitational microlensing, dark matter annihilation, planetary dynamics, resonance dynamics and exoplanet atmospheres. He has been described as a “general-purpose astrophysics theorist,” which he regards as quite a compliment.

Fun Fact: The computer code Jeremy used to make the black hole animations we featured last week is called “Pandurata,” after a species of black orchid from Sumatra. The name pays homage to the laser fusion lab at the University of Rochester where Jeremy worked as a high school student and wrote his first computer code, “Buttercup.” All the simulation codes at the lab are named after flowers.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Boo-tiful Ring Galaxies

A ghoulish secret lurks within each of these gorgeous galaxies. Their rings are dotted with stellar graveyards!

These objects are called ring galaxies, and scientists think most of them form in monster-sized crashes. Not just any galaxy collision will do the trick, though. To produce the treat of a ring, a smaller galaxy needs to ram through the center of a larger galaxy at just the perfect angle.

The collision causes ripples that disturb both galaxies. The gravitational shock causes dust, gas, and stars in the larger galaxy’s disk to rush outward. As this ring of material plows out from the galaxy’s center, gas clouds collide and trigger the birth of new stars.

In visible light, the blue areas in the galaxies’ rings show us where young, hot stars are growing up. Faint, pink regions around the ring mark stellar nurseries where even younger stars set hydrogen gas aglow.
The newborn stars come in a mix of sizes, from smaller ones like our Sun all the way up to huge stars with tens of times the Sun’s mass. And those massive stars live large!
While a star like our Sun will last many billions of years before running out of fuel, larger stars burn much brighter and faster. After just a few million years, the largest stars explode as supernovae. When massive stars die, they leave behind a stellar corpse, either a neutron star or black hole.

When we turn our X-ray telescopes to these ring galaxies, we see telltale signs of stellar remnants dotted throughout their ghostly circles. The purple dots in the X-ray image above are neutron stars or black holes that are siphoning off gas from a companion star, like a vampire. The gas reinvigorates stellar corpses, which heat up and emit X-rays. These gas-thirsty remains are beacons lighting the way to stellar graveyards.
Spiral galaxies — like our home galaxy, the Milky Way — have curved arms that appear to sweep out around a bright center. The dust and gas in those spiral arms press together, causing cycles of star formation that result in a more even mix of new stars and stellar corpses scattered throughout our galaxy. No creepy ring of stellar corpses here!
To visit some other eerie places in the universe, check out the latest additions to the Galaxy of Horrors poster series and follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook for news about black holes, neutron stars, galaxies, and all the amazing objects outside our solar system.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Happy New Year From NASA! The year 2021 was one for the books, so what will 2022 bring? No matter what, remember: You are made of star stuff. Sparkly, glorious star stuff.
What's this image? Click here. Credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA, A. Sarajedini Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
I still haven’t gotten over the fact that Hampshire College in Massachusetts has the worlds first non-human resident scholar.


THIS IS REAL

HOW IS THIS REAL



Stars, Sea, and Smoke from the ISS: Tournament Earth 2021
We started Tournament Earth with 32 photos taken by astronauts from the Interantional Space Station and now we are down to 8. All of the #1 seeds are gone. Two #8 seeds are dominating their groups. Who will win? Let's take a closer look at the competitors still in the game. Then remember to vote for your favorites. The champion will be announced on April 13, 2021.
Stars in Motion vs. Cleveland Volcano
This matchup pits smoke against stars, but both have interesting stories.

The International Space Station (ISS) is constantly in motion. For astronaut photographers on board, that motion has consequences. For one, it makes it challenging to take photos. The same motion makes it possible to shoot spectacular photos like the one above. The image is compiled from a series of photographs taken by astronaut Don Pettit while he was onboard the ISS in April 2012. This composite was made from more than 72 individual long-exposure photographs taken over several minutes as the ISS traveled over the Caribbean Sea, across South America, and over the South Atlantic Ocean.

Astronaut Jeff Williams was the first to witness activity at the Cleveland Volcano on May 3, 2006. The Cleveland Volcano is one of the most active in the Aleutian Islands, which extend west-southwest from the Alaska mainland. It is a stratovolcano composed of alternating layers of hardened lava, compacted volcanic ash, and volcanic rocks. The event proved to be short-lived; two hours later, the plume had completely detached from the volcano. The ash cloud height could have been as high as 6,000 meters (20,000 feet) above sea level.
Stargazing from the ISS vs. Cruising Past the Aurora Borealis
This is the most stellar matchup of the tournament, literally. Two beloved star pictures face off in what will be one of the most difficult choices of the tournament.

An astronaut took this broad, short-lens photograph of Earth’s night lights while looking out over the remote reaches of the central equatorial Pacific Ocean. The ISS was passing over the island nation of Kiribati at the time, about 2600 kilometers (1,600 miles) south of Hawaii. Scientists identified the pattern of stars in the photo as our Milky Way galaxy (looking toward its center). The dark patches are dense dust clouds in an inner spiral arm of our galaxy; such clouds can block our view of stars toward the center. The curvature of the Earth crosses the center of the image and is illuminated by a variety of airglow layers in orange, green, and red.

Commonly known as the northern lights, these colorful ribbons of light appear to dance in the sky over the planet’s high latitudes, attracting sky chasers and photographers. Astronaut Randy “Komrade” Bresnik shot this photograph on September 15, 2017, as the space station passed over Ontario, Canada. Curtains of green—the most familiar color of auroras—dominate the light show, with hints of purple and red.
Rolling Through the Appalachians vs. Castellanus Cloud Tower

The Susquehanna River cuts through the folds of the Valley-and-Ridge province of the Appalachian Mountains in this photograph taken from the International Space Station by astronaut Christina Koch. The Valley-and-Ridge province is a section of the larger Appalachian Mountain Belt between the Appalachian Plateau and the Blue Ridge physiographic provinces. The northeast-southwest trending ridges are composed of Early Paleozoic sedimentary rocks. The valleys between them were made of softer rocks (limestone and shales) that were more susceptible to erosion; they are now occupied by farms.

An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this photograph of a massive vertical cloud formation—known to meteorologists as cumulus castellanus—above Andros Island. The cloud name castellanus comes from the similarity to the crenellated towers or turrets of medieval castles. These clouds develop due to strong vertical air movement typically associated with thunderstorms.
Lake Van, Turkey vs. Typhoon Maysak from the Space Station

While orbiting on the International Space Station, astronaut Kate Rubins shot this photograph of part of Lake Van in Turkey, the largest soda or alkaline lake on Earth. Generally, soda lakes are distinguished by high concentrations of carbonate species. Lake Van is an endorheic lake—it has no outlet, so its water disappears by evaporation—with a pH of 10 and high salinity levels.

This photograph of super typhoon Maysak was taken by European Space Agency astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti as the International Space Station passed near the storm on March 31, 2015. The category 4 typhoon was headed for a possible landfall in the Philippines by the end of the week. It was unusual for the western Pacific to see such a strong storm so early in the year.
See all of the images and vote HERE. Follow @NASAEarth on social media for updates.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
“If you read the history of the development of chemistry and particularly of physics, you will see that even such exact natural sciences could not, and still cannot, avoid basing their thought systems on certain hypotheses. In classical physics, up to the end of the 18th century, one of the working hypotheses, arrived at either unconsciously or half-consciously, was that space had three dimensions, an idea which was never questioned. The fact was always accepted, and perspective drawings of physical events, diagrams, or experiments, were always in accordance with that theory. Only when this theory is abandoned does one wonder how such a thing could ever have been believed. How did one come by such an idea? Why were we so caught that nobody ever doubted or even discussed the matter? It was accepted as a self-evident fact, but what was at the root of it? Johannes Kepler, one of the fathers of modern or classic physics, said that naturally space must have three dimensions because of the Trinity! So our readiness to believe that space has three dimensions is a more recent offspring of the Christian trinitarian idea.”
— Marie-Louise von Franz, Alchemy: An Introduction to the Symbolism and the Psychology
Weird and Wonderful Irregular Galaxies
Spiral and elliptical galaxies seem neatly put together, but what happened to irregular galaxies? Irregular galaxies have one-of-a-kind shapes and many look like blobs! Why do they look the way they do? Astronomers think the uniqueness of these galaxies results from their interactions with other galaxies — like when they pass close to one another or even collide!

Looking back at the early universe with the help of our Hubble Space Telescope’s “deep field” observations, astronomers can peek at galaxies millions and billions of light-years away. They noticed that these far-away galaxies appear unusually messy, showing more star formation and mergers than galaxies closer to the Milky Way.

We also see irregular galaxies closer to home, though. Some may form when two galaxies pass close together in a near-miss. When this happens, their gravity pulls stars out of place in both galaxies, messing up the neat structure they originally had as spiral or elliptical galaxies. Think of it like this: you happen to have a pile of papers sitting at the edge of a table and when someone passes close by the papers become ruffled and may scatter everywhere! Even though the two galaxies never touched, gravity's effects leave them looking smeared or distorted.

Some irregular galaxies result from the collision between two galaxies. And while some of these look like a blob of stars and dust, others form dazzling ring galaxies! Scientists think these may be a product of collisions between small and large galaxies. These collisions cause ripples that disturb both galaxies, throwing dust, gas, and stars outward. When this happens, it pushes out a ring of material, causing gas clouds to collide and spark the birth of new stars. After just a few million years, stars larger than our Sun explode as supernovae, leaving neutron stars and black holes throughout the ring!

Not all galaxy collisions create irregular galaxies — our Milky Way spiral galaxy has gone through many mergers but has stayed intact! And for some interacting galaxies, being an irregular galaxy may just be a phase in their transformation. We’re observing them at a snapshot in time where things are messy, but they may eventually become neat and structured spirals and ellipticals.

Irregular galaxies are similar to each other, but unique and beautiful because of their different interactions, whether they’re just passing another galaxy or taking part in a dramatic collision. Keep up with NASA Universe on Facebook and Twitter where we post regularly about galaxies.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

NASA Spotlight: Astronaut Soichi Noguchi
Soichi Noguchi was selected as an astronaut with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency in 1996. A native of Yokohama, Kanagawa, he is currently a mission specialist for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 launch taking flight to the International Space Station on Nov. 14. Soichi will be the first international crewmember on Crew Dragon and the first international partner astronaut to fly aboard three types of orbital spacecraft – the U.S. space shuttle, the Russian Soyuz, and now the SpaceX Crew Dragon! Talk about impressive. He received a B.S. in Aeronautical Engineering in 1989, master’s degree in Aeronautical Engineering in 1991, Doctor of Philosophy in Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies in 2020, all from the University of Tokyo.
Soichi took time from preparing for his historic mission to answer questions about his life and career:
You recently earned a doctorate in philosophy. What made you do it?
After my second flight, I started this research about your sensory system in zero gravity. I used a my own personal video, which I took during my last two flights at the International Space Station. I had a lot of interesting discussions amongst young professionals and students at the University of Tokyo about the research. It was a fun experience – but I would not do it again!
Space is a risky business. Why do it?
Space IS definitely a risky business. But the reward is higher than the risk so that’s why we take it.
Do you have a message for boys and girls in Japan who are interested in science and engineering?
Three words: Space. Is. Waiting.

Aside from mission objectives and tasks, what’s a personal goal for this mission?
We have a lot of interesting missions to do, but my personal goal is to return home with lots of fun stories.

What was it like to get the phone call to become an astronaut?
It was 25 years ago, but I still remember the voice vividly. I got a call from Dr. Mamoru Mohri, the very first JAXA astronaut, and he said “Welcome to the Astronaut Corps.” When I got the call to be part of the Crew-1 mission, I was a lot less nervous than when I was assigned to my first mission, but the excitement remains the same.
Can you describe your crew mate Mike Hopkins in one sentence?
He is a natural leader that takes care of the team really well, and he’s fun to play around with.

Star Trek or Star Wars?
Star Wars… just because!

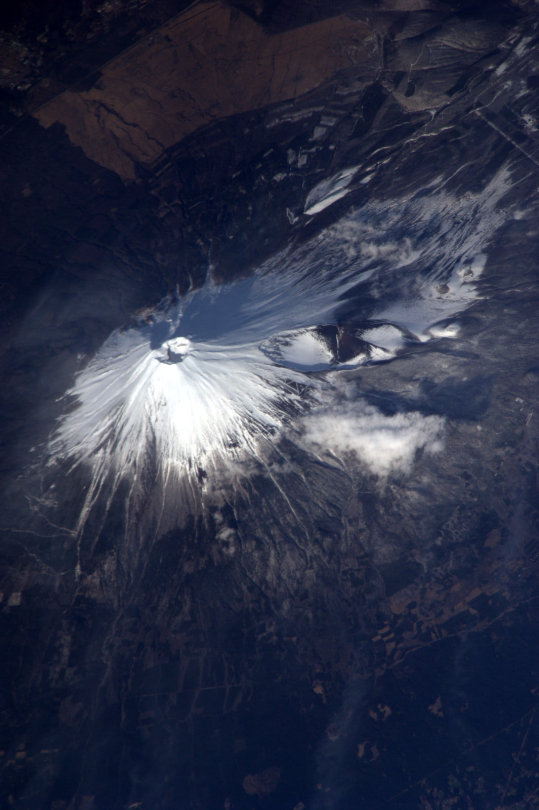
Can you share your favorite photo or video that you took in space?
My favorite photo is Mount Fuji because I see the mountain almost every day when I was a child. It’s definitely breathtaking to see Mount Fuji from space.

What personal items did you decide to pack for launch and why?
I have lots of family photos, and I would put it inside my sleep station. Definitely one of the most challenging things about spaceflight is not experiencing zero gravity, not the rocket, but time away from family.
How would you describe spacewalking outside the space station?
It’s an excursion. The view of the Earth is just breathtaking because you are just one glass away from the vacuum of space. There’s nothing between you and Earth.

What are you most excited about for the future of human space exploration?
I would say I’m most excited for interplanetary travel to become more common so that the school kids can go to Mars on their field trip.
What would you say to someone looking to follow in your footsteps?
Don’t worry, be happy!
How has spaceflight evolved since your first launch and stay aboard the International Space Station in 2005?
This is definitely an exciting moment. We’re starting to see more players in the game. SpaceX is the frontrunner, but soon we’ll see Boeing, Sierra Nevada and Axiom. So the International Space Station will soon have more players involved, and it will be a lot more fun!
Thank you for your time, Soichi, and good luck on your historic mission! Get to know a bit more about Soichi and his NASA astronaut crew mates Victor Glover, Michael Hopkins, and Shannon Walker in the video above.
Watch LIVE launch coverage beginning at 3:30 p.m. EST on Nov. 14 HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 seaside-savannah reblogged this · 6 months ago
seaside-savannah reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 maaltajik liked this · 8 months ago
maaltajik liked this · 8 months ago -
 reolitreace liked this · 1 year ago
reolitreace liked this · 1 year ago -
 chachito555 liked this · 1 year ago
chachito555 liked this · 1 year ago -
 redundare liked this · 2 years ago
redundare liked this · 2 years ago -
 albabutter reblogged this · 2 years ago
albabutter reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 stonerock liked this · 2 years ago
stonerock liked this · 2 years ago -
 alwaysbookedfanfictionresearch reblogged this · 2 years ago
alwaysbookedfanfictionresearch reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 alwaysbookedfanfictionresearch liked this · 2 years ago
alwaysbookedfanfictionresearch liked this · 2 years ago -
 vanderlysposts liked this · 2 years ago
vanderlysposts liked this · 2 years ago -
 hayley-hoot194500-blog liked this · 3 years ago
hayley-hoot194500-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 cpngohst liked this · 3 years ago
cpngohst liked this · 3 years ago -
 appla1 reblogged this · 3 years ago
appla1 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 serenje liked this · 3 years ago
serenje liked this · 3 years ago -
 smirkydimple liked this · 3 years ago
smirkydimple liked this · 3 years ago -
 hawaiianlungs liked this · 3 years ago
hawaiianlungs liked this · 3 years ago