House Of Horrors: Exoplanet Edition
House of Horrors: Exoplanet Edition
Astronomers may be closer than ever to discovering a planet that’s habitable like our own, but along the way they’ve discovered some very scary exoplanets – places where conditions are far too harsh for life as we know it to exist.
Okay, but what IS an exoplanet???

We’ve rounded up some of the most frightening, deadly exoplanets, places that make even the scariest haunted house on Earth pale in comparison. Check them out...
Radiation Bath, Anyone?
The exoplanets PSR B1257+12 B, C & D were among the first discovered, and also happened to be three of the weirdest! The entire system is a graveyard, remnants of what used to be a normal, functional solar system before the star blew apart in a giant explosion known as a supernova.

The massive shockwave from the supernova stripped away any atmosphere or living creatures that might have once lived on these planets, leaving behind ghostly, rocky shells, dead planets orbiting the corpse of an extinct star.
Except that the system isn’t completely dead…the remaining core from the old star has become a zombie star called a pulsar. Literally spinning in its grave, it makes a full rotation every 6.22 milliseconds and emits an intense beam of radiation that can be detected from Earth. The star’s unfortunate planets are thus bathed in deadly radiation on a regular basis, making sure that this system remains a cosmic no-man’s land.
A Mighty Wind
The sound of howling wind is a must for any Earth-based haunted house, but weather conditions on HD 189733 b make it a very dangerous place to go trick-or-treating.
At first glance, this exoplanet looks like the typical “hot Jupiter” — a huge gas planet perched dangerously to a burning-hot star, with daytime temperatures around a balmy 1,770 degrees Fahrenheit. This exoplanet is also “tidally locked” in its orbit, which means that the same side of the planet always faces its star.

But when scientists measured the planet’s nighttime temperature, they were shocked to find that it was only 500 degrees cooler. How does the back side of the planet stay so warm?
The answer is wind! Insanely fast, dangerous wind that whisks heat from day-side to night-side at a speed of 4,500 mph, nearly six times the speed of sound! In fact, astronomers estimate that wind speeds might top out at 5,400 mph, conditions that make hurricanes on Earth look like a breezy day at the beach.
Newborn Exoplanet Around Scorching Star
This exoplanet, named K2-33b, is the youngest fully formed exoplanet ever detected. This planet is a bit larger than Neptune and whips tightly around its star every five days. Since this planet sits nearly 10 times closer to its star than Mercury is to our sun, it’s HOT!

No matter how cute you think infants are, this is one baby you’d want to stay away from.
Boil, Boil, Toil and Trouble
The planet HD 209458 b (aka. Osiris - the god of death) has a few things in common with Earth: water vapor, methane and carbon dioxide in its atmosphere, key ingredients for life on our planet. Don’t be fooled, though, because this planet is a rolling cauldron of almost unimaginable heat.

Even the hottest summer days on Earth don’t get as dangerous as the conditions here. A planet that orbits so close to its host star that its atmosphere is literally boiling off, ripped away from the planet as it whips around on its breakneck 3.5-day orbit.
All Alone and Very, Very Cold
While most of the exoplanets found so far are hellishly hot, OGLE-2005-BLG-390L b has the distinction of being extremely cold.
The planet takes about 10 Earth years to orbit its tiny dwarf star, and it’s a chilly trip; the average temperature on this exoplanet is 50 Kelvin, or minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit! A good costume for trick-or-treating on this frigid planet would be a toasty self-heating spacesuit, an oxygen supply, ice skates and plenty of hot cocoa.

Of course, don’t expect to find many houses with candy here, because despite the fact that it’s just a few times bigger than Earth, this exoplanet is an uninhabitable ice ball stuck in a perpetual winter freeze.
A Scorched World
Kepler-10b is a scorched world, orbiting at a distance that’s more than 20 times closer to its star than Mercury is to our own sun. The daytime temperatures are expected to be more than 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit, hotter than lava flows here on Earth.

Intense radiation from the star has kept the planet from holding onto an atmosphere, but flecks of silicates and iron that have boiled off a molten surface are swept away by the stellar radiation.
Learn more about worlds beyond our solar system at: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
How Exactly Do We Plan to Bring an Asteroid Sample Back to Earth?
Our OSIRIS-REx spacecraft launches tomorrow, and will travel to a near-Earth asteroid, called Bennu. While there, it will collect a sample to bring back to Earth for study. But how exactly do we plan to get this spacecraft there and bring the sample back?

Here’s the plan:
After launch, OSIRIS-REx will orbit the sun for a year, then use Earth’s gravitational field to assist it on its way to Bennu. In August 2018, the spacecraft’s approach to Bennu will begin.

The spacecraft will begin a detailed survey of Bennu two months after slowing to encounter the asteroid. The process will last over a year, and will include mapping of potential sample sites. After the selection of the final site, the spacecraft will briefly touch the surface of Bennu to retrieve a sample.

To collect a sample, the sampling arm will make contact with the surface of Bennu for about five seconds, during which it will release a burst of nitrogen gas. The procedure will cause rocks and surface material to be stirred up and captured in the sampler head. The spacecraft has enough nitrogen to allow three sampling attempts, to collect between 60 and 2000 grams (2-70 ounces).

In March 2021, the window for departure from the asteroid will open, and OSIRIS-REx will begin its return journey to Earth, arriving two and a half years later in September 2023.

The sample return capsule will separate from the spacecraft and enter the Earth’s atmosphere. The capsule containing the sample will be collected at the Utah Test and Training Range.

For two years after the sample return, the science team will catalog the sample and conduct analysis. We will also preserve at least 75% of the sample for further research by scientists worldwide, including future generations of scientists.
The Spacecraft

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is outfitted with some amazing instruments that will help complete the mission. Here’s a quick rundown:
The OCAMS Instrument Suite

PolyCam (center), MapCam (left) and SamCam (right) make up the camera suite on the spacecraft. These instruments are responsible for most of the visible light images that will be taken by the spacecraft.
OSIRIS-REx Laser Altimeter (OLA)

This instrument will provide a 3-D map of asteroid Bennu’s shape, which will allow scientists to understand the context of the asteroid’s geography and the sample location.
OSIRIS-REx Thermal Emission Spectrometer (OTES)

The OTES instrument will conduct surveys to map mineral and chemical abundances and will take the asteroid Bennu’s temperature.
OSIRIS-REx Visible and Infrared Spectrometer (OVIRS)

This instrument will measure visible and near infrared light from the asteroid. These observations could be used to identify water and organic materials.
Regolith X-Ray Imaging Spectrometer (REXIS)

REXIS can image X-ray emission from Bennu in order to provide an elemental abundance map of the asteroid’s surface.
Touch-and-Go Sample Arm Mechanism (TAGSAM)

This part of the spacecraft will be responsible for collecting a sample from Bennu’s surface.
Watch Launch and More!

OSIRIS-REx Talk Wednesday, Sept. 7 at noon EDT Join us for a discussion with representatives from the mission’s science and engineering teams. This talk will include an overview of the spacecraft and the science behind the mission. Social media followers can ask questions during this event by using #askNASA. Watch HERE.
Uncovering the Secrets of Asteroids Wednesday, Sept. 7 at 1 p.m. EDT During this panel, our scientists will discuss asteroids, how they relate to the origins of our solar system and the search for life beyond Earth. Social media followers can ask questions during this event by using #askNASA. Watch HERE.
LAUNCH COVERAGE!
Thursday, Sept. 8 starting at 5:30 p.m. EDT Watch the liftoff of the United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:05 p.m.
Full coverage is available online starting at 4:30 p.m. Watch HERE
We will also stream the liftoff on Facebook Live starting at 6:50 p.m. EDT. Watch HERE
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What would happen if a Black hole would be near the earth? What would be the consequences to humans?
10 Things to Know About Explorer 1, America's First Satellite
Sixty years ago, the hopes of Cold War America soared into the night sky as a rocket lofted skyward above Cape Canaveral, a soon-to-be-famous barrier island off the Florida coast.
1. The Original Science Robot

Sixty years ago this week, the United States sent its first satellite into space on Jan. 31, 1958. The spacecraft, small enough to be held triumphantly overhead, orbited Earth from as far as 1,594 miles (2,565 km) above and made the first scientific discovery in space. It was called, appropriately, Explorer 1.
2. Why It's Important

The world had changed three months before Explorer 1's launch, when the Soviet Union lofted Sputnik into orbit on Oct. 4, 1957. That satellite was followed a month later by a second Sputnik spacecraft. All of the missions were inspired when an international council of scientists called for satellites to be placed in Earth orbit in the pursuit of science. The Space Age was on.
3. It...Wasn't Easy

When Explorer 1 launched, we (NASA) didn't yet exist. It was a project of the U.S. Army and was built by Caltech's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. After the Sputnik launch, the Army, Navy and Air Force were tasked by President Eisenhower with getting a satellite into orbit within 90 days. The Navy's Vanguard Rocket, the first choice, exploded on the launch pad Dec. 6, 1957.
4. The People Behind Explorer 1

University of Iowa physicist James Van Allen, whose proposal was chosen for the Vanguard satellite, had made sure his scientific instrument—a cosmic ray detector—would fit either launch vehicle. Wernher von Braun, working with the Army Ballistic Missile Agency in Alabama, directed the design of the Redstone Jupiter-C launch rocket, while JPL Director William Pickering oversaw the design of Explorer 1 and other upper stages of the rocket. JPL was also responsible for sending and receiving communications from the spacecraft.
5. All About the Science

Explorer 1's science payload took up 37.25 inches (95 cm) of the satellite's total 80.75 inches (2.05 meters). The main instruments were a cosmic-ray detector; internal, external and nose-cone temperature sensors; a micrometeorite impact microphone; a ring of micrometeorite erosion gauges; and two transmitters. There were two antennas in the body of the satellite and its four flexible whips formed a turnstile antenna that extended with the rotation of the satellite. Electrical power was provided by batteries that made up 40 percent of the total payload weight.
6. At the Center of a Space Doughnut

The first scientific discovery in space came from Explorer 1. Earth is surrounded by radiation belts of electrons and charged particles, some of them moving at nearly the speed of light, about 186,000 miles (299,000 km) per second. The two belts are shaped like giant doughnuts with Earth at the center. Data from Explorer 1 and Explorer 3 (launched March 26, 1958) led to the discovery of the inner radiation belt, while Pioneer 3 (Dec. 6, 1958) and Explorer IV (July 26, 1958) provided additional data, leading to the discovery of the outer radiation belt. The radiation belts can be hazardous for spacecraft, but they also protect the planet from harmful particles and energy from the Sun.
7. 58,376 Orbits

Explorer 1's last transmission was received May 21, 1958. The spacecraft re-entered Earth's atmosphere and burned up on March 31, 1970, after 58,376 orbits. From 1958 on, more than 100 spacecraft would fall under the Explorer designation.
8. Find Out More!

Want to know more about Explorer 1? Check out the website and download the poster celebrating 60 years of space science. go.nasa.gov/Explorer1
9. Hold the Spacecraft In Your Hands

Create your own iconic Explorer 1 photo (or re-create the original), with our Spacecraft 3D app. Follow @NASAEarth this week to see how we #ExploreAsOne. https://go.nasa.gov/2BmSCWi
10. What's Next?

All of our missions can trace a lineage to Explorer 1. This year alone, we're going to expand the study of our home planet from space with the launch of two new satellite missions (GRACE-FO and ICESat-2); we're going back to Mars with InSight; and the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will search for planets outside our solar system by monitoring 200,000 bright, nearby stars. Meanwhile, the Parker Solar Probe will build on the work of James Van Allen when it flies closer to the Sun than any mission before.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Why do scientists think there could have been life on Mars?
What’s Up for April 2016?

Jupiter, Mars, the Lyrid meteor shower and 2016’s best views of Mercury are all visible in the sky this month.

Jupiter, where our Juno mission will begin orbiting on July 4, continues to shine almost as brightly this month as last. And eagle-eyed telescope viewers will see a transit, a shadow transit, an occultation and an eclipse of Jupiter’s moons- all in one night: April 6-7.

Io transits first, crossing the planet beginning at 9:52 p.m. EDT. It’s shadow can be seen less than an hour later.

Next Jupiter occults, or eclipses, Europa as Europa slips behind the giant planet at 10:48 p.m. EDT. At 3 a.m. Europa reappears from its eclipse, dramatically leaving the shadow of Jupiter.

Ganymede transits the planet beginning at 1:01 EDT April 7.
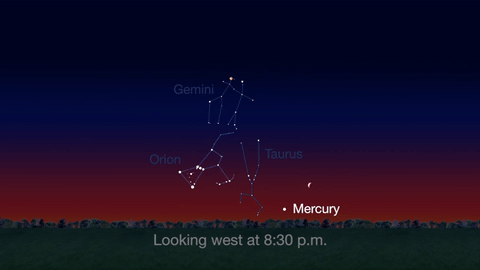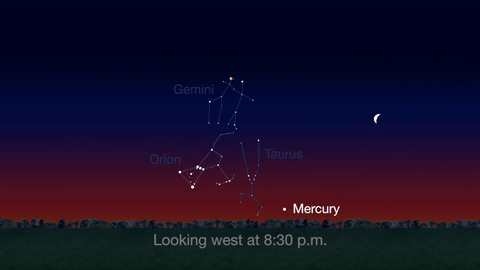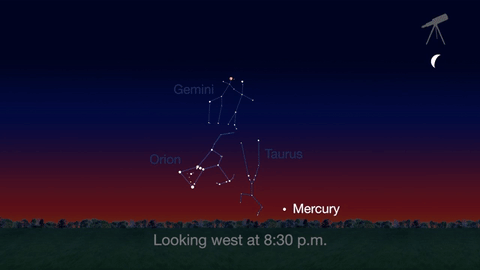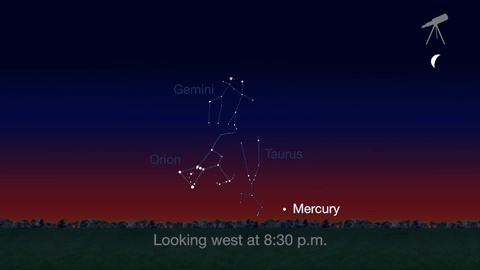
Check out the other planets in April, too! Mercury is always a challenging object to view, but this month you can spot it after sunset about 10 degrees above the horizon. Through a telescope you can see its phase. It will appear like a tiny crescent moon, with about 1/3 of its disk illuminated.

Mars is finally visible before midnight this month. It rises in the southeast at about 10 p.m. by the end of April. The best observing of Mars will be when it is highest in the sky. This means a few hours before dawn. Its brightness and apparent size increase dramatically this month. By month’s end, Mars appears nearly twice as bright as at the beginning of the month.

About mid-month you’ll see Mars near its rival in the sky: the similar-colored red supergiant star Antares. The name “Antares” means “equal to or rival of Mars”.
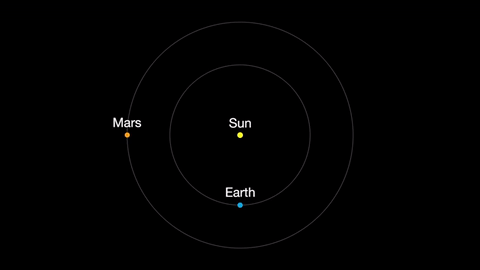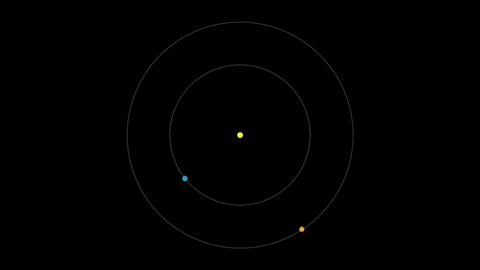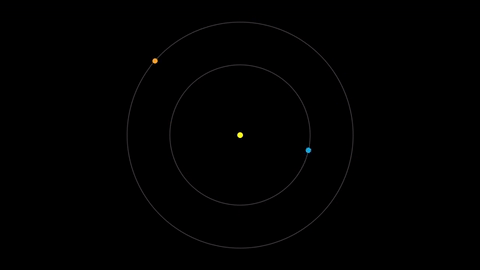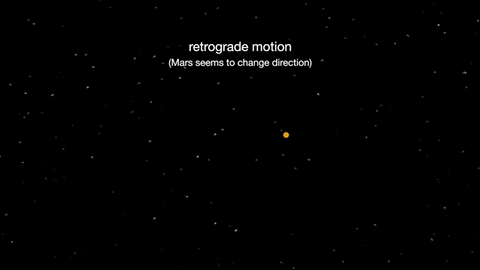
Earth moves almost twice as fast as Mars does, so it often passes Mars in their race around the sun. This causes “retrograde motion”: an illusion we see from our viewpoint on Earth.
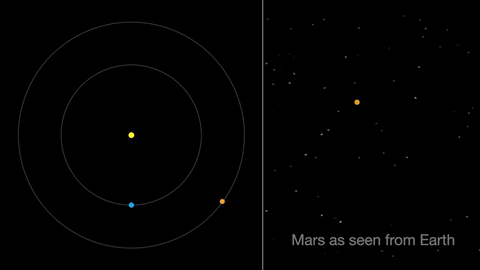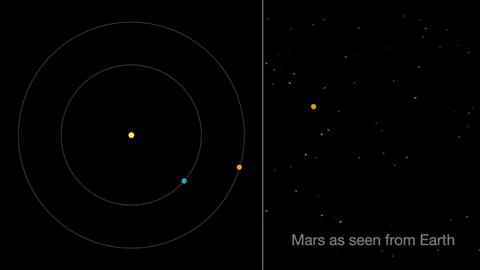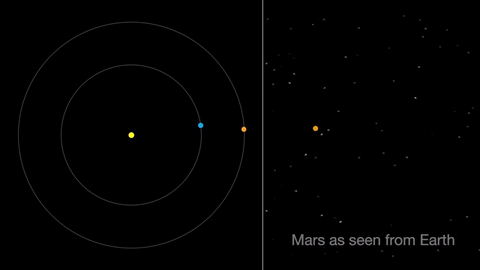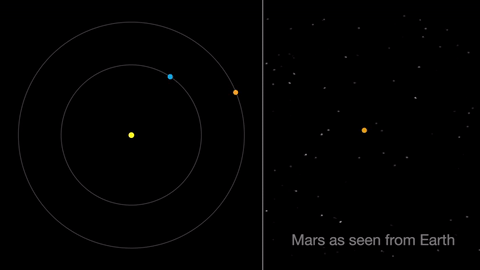
Retrograde motion happens as Earth catches up to Mars, causing Mars to appear slow to slow its eastward motion against the stars. After a few days, when Earth has overtaken Mars, the Red Planet seems to move westward. Eventually, Earth moves far enough around its orbit that Mars appears to be moving eastward again.
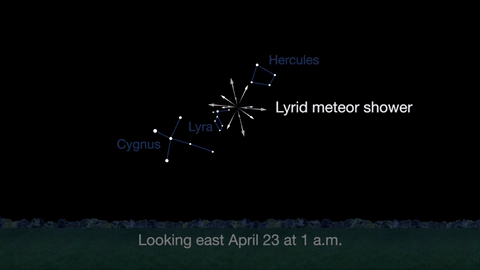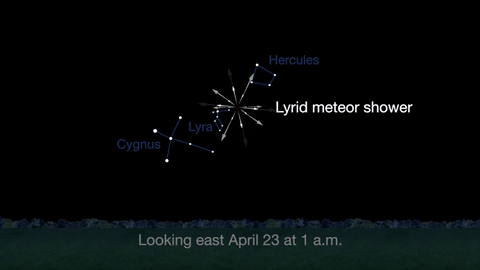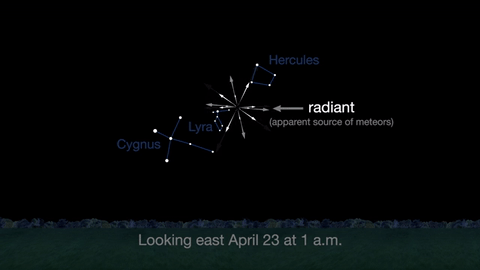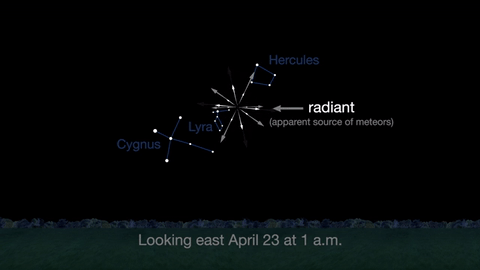
April features one meteor shower, the Lyrids. This year the Lyrids are marred by the full moon. The best time to view will be just before dawn on April 23, when the constellation Lyra is overhead and the moon will be near to setting.
With all of these great things to spot in the sky this month, be sure to get outside and look up!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Photograph of the Apollo 13 Spacecraft Being Returned to the Prime Recovery Ship, USS Iwo Jima, 4/17/1970
Series: Color Photograph Files, 1965 - 2002. Record Group 255: Records of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1903 - 2006.
Apollo 13 was intended to be the third Apollo mission to land on the Moon. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Florida on April 11, 1970. Two days into the flight, damaged wire insulation inside the oxygen tank in the service module ignited, causing an explosion which vented the oxygen tank into space. Without oxygen, the service module became inoperable and the lunar mission quickly turned into a mission to safely return the crew to Earth. The astronauts worked with Mission Control to shut down the command module in order to conserve the remaining oxygen, forcing all three astronauts into the lunar module. The astronauts continued to work with Mission Control to combat one technical failure after another until, on April 17, 1970, the crew landed safely in the South Pacific Ocean.
source: phillyarchives.tumblr.com

Thanks everyone for your fantastic questions! Sorry I couldn’t answer all of them. I hope you have fun on Monday, Aug. 21st and share your photos and experiences with us! https://www.flickr.com/groups/nasa-eclipse2017/
Safe viewing and talk to you later! https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/safety
New Sun Science Stamps from the U.S. Postal Service
To start off the summer, the U.S. Postal Service issued a set of stamps showcasing views of the Sun from our Solar Dynamics Observatory!

Since its launch in 2010, the Solar Dynamics Observatory (or SDO) has kept up a near-constant watch on the Sun from its vantage point in orbit around Earth. SDO watches the Sun in more than 10 different types of light, including some that are absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere so can only be seen from space. These different types of light allow scientists to study different parts of the Sun – from its surface to its atmosphere – and better understand the solar activity that can affect our technology on Earth and in space.

The new set of stamps features 10 images from SDO. Most of these images are in extreme ultraviolet light, which is invisible to human eyes.
Let’s explore the science behind some of the stamps!
Coronal hole (May 2016)

The dark area capping the northern polar region of the Sun is a coronal hole, a magnetically open area on the Sun from which high-speed solar wind escapes into space. Such high-speed solar wind streams can spark magnificent auroral displays on Earth when they collide with our planet’s magnetic field.
Solar flare (August 2011)

The bright flash on the Sun’s upper right is a powerful solar flare. Solar flares are bursts of light and energy that can disturb the part of Earth’s atmosphere where GPS and radio signals travel.
Active Sun (October 2014)

This view highlights the many active regions dotting the Sun’s surface. Active regions are areas of intense and complex magnetic fields on the Sun – linked to sunspots – that are prone to erupting with solar flares or explosions of material called coronal mass ejections.
Plasma blast (August 2012)

These images show a burst of material from the Sun, called a coronal mass ejection. These eruptions of magnetized solar material can create space weather effects on Earth when they collide with our planet’s magnetosphere, or magnetic environment – including aurora, satellite disruptions, and, when extreme, even power outages.
Coronal loops (July 2012)

These images show evolving coronal loops across the limb and disk of the Sun. Just days after these images were taken, the Sun unleashed a powerful solar flare.
Coronal loops are often found over sunspots and active regions, which are areas of intense and complex magnetic fields on the Sun.
Sunspots (October 2014)

This view in visible light – the type of light we can see – shows a cluster of sunspots near the center of the Sun. Sunspots appear dark because they are relatively cool compared to surrounding material, a consequence of the way their extremely dense magnetic field prevents heated material from rising to the solar surface.
For more Sun science, follow NASA Sun on Twitter, on Facebook, or on the web.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Three Ways to Travel at (Nearly) the Speed of Light

One hundred years ago, Einstein’s theory of general relativity was supported by the results of a solar eclipse experiment. Even before that, Einstein had developed the theory of special relativity — a way of understanding how light travels through space.
Particles of light — photons — travel through a vacuum at a constant pace of more than 670 million miles per hour.

All across space, from black holes to our near-Earth environment, particles are being accelerated to incredible speeds — some even reaching 99.9% the speed of light! By studying these super fast particles, we can learn more about our galactic neighborhood.
Here are three ways particles can accelerate:
1) Electromagnetic Fields!
Electromagnetic fields are the same forces that keep magnets on your fridge! The two components — electric and magnetic fields — work together to whisk particles at super fast speeds throughout the universe. In the right conditions, electromagnetic fields can accelerate particles at near-light-speed.

We can harness electric fields to accelerate particles to similar speeds on Earth! Particle accelerators, like the Large Hadron Collider and Fermilab, use pulsed electromagnetic fields to smash together particles and produce collisions with immense amounts of energy. These experiments help scientists understand the Big Bang and how it shaped the universe!
2) Magnetic Explosions!

Magnetic fields are everywhere in space, encircling Earth and spanning the solar system. When these magnetic fields run into each other, they can become tangled. When the tension between the crossed lines becomes too great, the lines explosively snap and realign in a process known as magnetic reconnection. Scientists suspect this is one way that particles — for example, the solar wind, which is the constant stream of charged particles from the Sun — are sped up to super fast speeds.

When magnetic reconnection occurs on the side of Earth facing away from the Sun, the particles can be hurled into Earth’s upper atmosphere where they spark the auroras.
3) Wave-Particle Interactions!

Particles can be accelerated by interactions with electromagnetic waves, called wave-particle interactions. When electromagnetic waves collide, their fields can become compressed. Charged particles bounce back and forth between the waves, like a ball bouncing between two merging walls. These types of interactions are constantly occurring in near-Earth space and are responsible for damaging electronics on spacecraft and satellites in space.

Wave-particle interactions might also be responsible for accelerating some cosmic rays from outside our solar system. After a supernova explosion, a hot, dense shell of compressed gas called a blast wave is ejected away from the stellar core. Wave-particle interactions in these bubbles can launch high-energy cosmic rays at 99.6% the speed of light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How do space plants grow? This experiment on the International Space Station hopes to find out. Space-grown plants look mostly normal, but have some distinct features compared to plants grown on Earth – most notably in the way their roots grow.
Roots evolved to grow “down” to search out nutrients and water, and on Earth, that response is predominantly governed by the force of gravity. But how does a plant know which way is down when there is no “down”? What determines the direction in which the plant’s roots should grow in space?
We are studying the molecular genetic signals that help guide plant growth in the novel environment of spaceflight, including how plants use new molecular “tools” to sense and respond to their environment when familiar signals are absent. What we learn could improve the way we grow plants in microgravity on future space missions, enabling crews to use plants for food and oxygen. This is just one of many petri plates filled with tiny plants from the Characterizing Arabidopsis Root Attractions-2 (CARA-2) that was recently harvest aboard the space station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 bugeyedcreature reblogged this · 2 years ago
bugeyedcreature reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 bugeyedcreature reblogged this · 2 years ago
bugeyedcreature reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 bugeyedcreature liked this · 2 years ago
bugeyedcreature liked this · 2 years ago -
 sublimedreamercreatorpeach-blog liked this · 4 years ago
sublimedreamercreatorpeach-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 redsplatterpaint liked this · 5 years ago
redsplatterpaint liked this · 5 years ago -
 1amtheh1ghway reblogged this · 5 years ago
1amtheh1ghway reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 1amtheh1ghway liked this · 5 years ago
1amtheh1ghway liked this · 5 years ago -
 fahidbaby liked this · 5 years ago
fahidbaby liked this · 5 years ago -
 ottobooty reblogged this · 5 years ago
ottobooty reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mekkababble liked this · 5 years ago
mekkababble liked this · 5 years ago -
 hunterraider reblogged this · 5 years ago
hunterraider reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lioness--hart reblogged this · 5 years ago
lioness--hart reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 moribirb liked this · 6 years ago
moribirb liked this · 6 years ago -
 cookies-and-berries reblogged this · 6 years ago
cookies-and-berries reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cookies-and-berries liked this · 6 years ago
cookies-and-berries liked this · 6 years ago -
 royal-crypt reblogged this · 6 years ago
royal-crypt reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 brujaprieta liked this · 6 years ago
brujaprieta liked this · 6 years ago -
 damnnashy liked this · 7 years ago
damnnashy liked this · 7 years ago -
 holleringpogs reblogged this · 8 years ago
holleringpogs reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 m00ndingochan liked this · 8 years ago
m00ndingochan liked this · 8 years ago -
 aslimewithagun liked this · 8 years ago
aslimewithagun liked this · 8 years ago -
 maychild liked this · 8 years ago
maychild liked this · 8 years ago -
 claudiomarco85-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
claudiomarco85-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 l4stb0y liked this · 8 years ago
l4stb0y liked this · 8 years ago -
 coralide reblogged this · 8 years ago
coralide reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 best-hotels-posts reblogged this · 8 years ago
best-hotels-posts reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 alfred-the-batler liked this · 8 years ago
alfred-the-batler liked this · 8 years ago -
 faineant-eater reblogged this · 8 years ago
faineant-eater reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tomlinsol reblogged this · 8 years ago
tomlinsol reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 perpetualanhedonia reblogged this · 8 years ago
perpetualanhedonia reblogged this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts