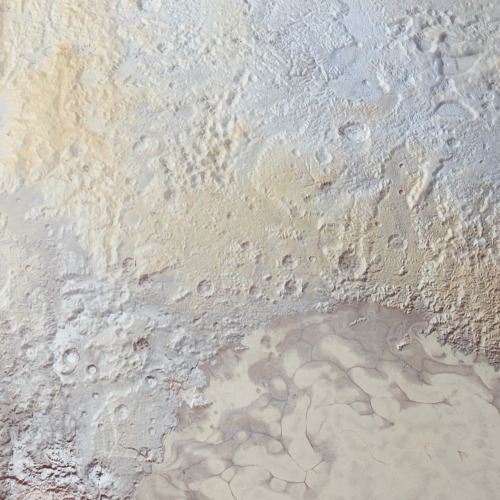
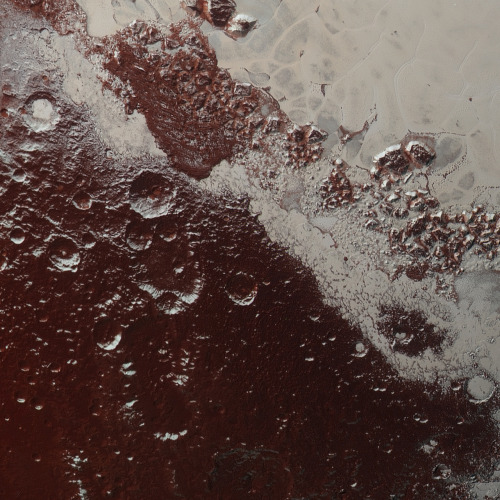
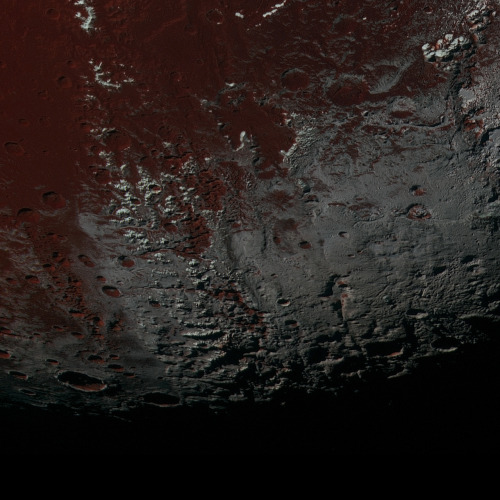
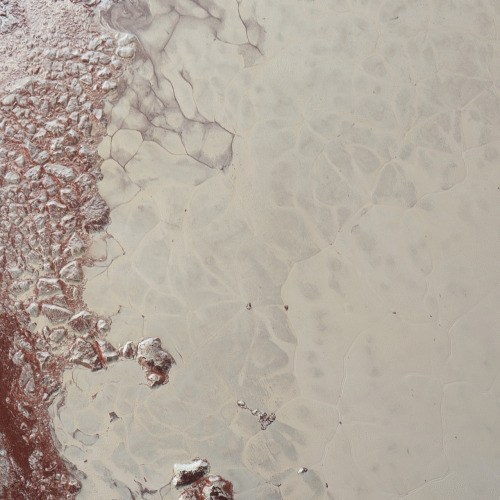
Eagle Nebula

Eagle Nebula
via reddit
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others

In the ancient world (and, honestly, today too) there’s nothing spookier than the sky doing something weird. Auroras, meteors, comets, and eclipses all fell under the category of scary, prophetic bad omens, but don’t worry! In this podcast I explain what they are! There are also some opportunities to see these astronomical events in action coming up. The annual Perseid meteor shower reaches its peak August 11-13 and there will be a total eclipse of the Sun (or a partial eclipse, depending where you’re viewing it from) across North America on August 21, 2017.
Below the cut are sources, music credits, vocabulary list, and the transcript of this episode. Check out the glossary, it’s a big one! There are also some cool eclipse-viewing resources I’ll highlight so you can view this phenomenon safely.
Let me know what you think I should research by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me in real life. And please check out the podcast on iTunes, rate it or review it if you’d like, subscribe, and maybe tell your friends about it if you think they’d like to listen!
(My thoughts on the next episode were spectroscopy, probes through the ages, and the transit of Venus. Let me know by the 2nd and I’ll have the next podcast up on August 14th, barring any delays due to trip fatigue!)
Glossary
auroras - a light display that occurs when a magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by solar wind that charged particles scatter into the upper atmosphere and lose their energy.
comet - a small, icy body that orbits the Sun. When its orbit takes it close to the Sun, the comet warms up and releases gases and debris that produce a visible atmosphere, sometimes called the comet’s tail.
corona - the hot outer atmosphere of the Sun.
eclipse - when three celestial bodies line up so that one obstructs the visibility of the other two. A solar eclipse can be partial (only part of the Sun is obscured by the Moon), total (all of the Sun is hidden by the Moon), or annular ( the Moon is close to Earth and appears too small to completely cover the Sun completely).
Exeligmos cycle - a cycle that is 3 times the saros cycle, or 669 months. It is more accurate means of predicting eclipses and additionally predicts eclipses that will be visible from a location close to the initial eclipse.
Inex cycle - a cycle of 28 years and 345 days long used to predict an eclipse that’s visible in the opposite hemisphere. For example, if an eclipse happens in the Northern hemisphere, one Inex cycle later there will be an eclipse visible in the Southern hemisphere. The Inex cycle does not ensure that both kinds of eclipses will be of the same type.
meteor - a small rocky or metallic body in space, smaller than asteroids. Contact with the Earth’s atmosphere causes a meteor to burn up in a streak of light. Many meteors entering the atmosphere within a few minutes of each other is called a meteor shower. If a meteor impacts on Earth’s surface without burning up, it is then classified as a meteorite.
penumbra - a region where only a portion of the light source is obscured. When the light source is completely blocked, this darkest part of a shadow is called the umbra.
perihelion - an object’s closest approach to the Sun in its orbit. Its greatest distance from the Sun is called its aphelion.
perigee - a satellite’s closest approach to the Earth in its orbit. Its greatest distance from Earth is called its apogee.
radiant - the point in the sky where objects appear to come from. For example, the Perseid meteor shower appears to come from the constellation Perseus.
Saros cycle - a cycle of 223 months that is used to predict eclipses.
solar prominence - a large, bright feature anchored to the Sun's surface and extend outwards into the Sun's corona. A prominence forms in about a day out of plasma, a hot gas made of electrically charged hydrogen and helium. Stable prominences may last for several months, looping hundreds of thousands of miles into space as plasma flows along a structure of the Sun’s magnetic field that has burst outward, releasing the plasma.
syzygy - the straight-line alignment of three celestial bodies.
Script/Transcript
Sources
Perseids via EarthSky
Perseids via NASA
Meteor showers and viewing tips via StarDate
Comet Swift-Tuttle via NASA
My local library’s information and recommended reading list for learning about eclipses. Love you, Multnomah County!
Map of the Path of Totality across the United States
Solar eclipse map and calendar via the Exploratorium website
Free eclipse glasses at libraries via Lunar and Planetary Institute
Guide to making a pinhole camera to view the eclipse via NASA
Historical eclipses via NASA
Historical eclipses via Astronomy Magazine
“Even if the Moon, however, does sometimes cover the Sun entirely, the eclipse does not have duration or extension; but a kind of light is visible about the rim which keeps the shadow from being profound and absolute.”
Solar prominence via NASA
Solar flares via NASA
Fred Espenak’s guide to eclipses. He’s a former NASA astrophysicist who’s credited with all the eclipse predictions so I trust him.
Some good but confusing charts on solar eclipse Saros cycles via NASA
“Van den Bergh placed all 8,000 solar eclipses in von Oppolzer's Canon der Finsternisse (1887) into a large two-dimensional matrix. Each Saros series was arranged as a separate column containing every eclipse in chronological order. The individual Saros columns were then staggered so that the horizontal rows each corresponded to different Inex series.”
A Danish webpage on calculating eclipses
Hawks, Ellison. The Boy’s Book of Astronomy. Frederick A. Stokes Co: New York, 1914. Located in Google Books preview. (Heads up, this is a fairly racist source.)
Richard Cohen. Chasing the Sun. Random House: NY, 2010.
Robert A. Henning: “different forms, wavering, many colours diffusing and changing, sometimes far away, sometimes filling the heavens around and above, plunging great dropping spears and sheets of colour earthward towards your very head as though a great hand were dropping colour like burning oil” (43).
Ernest W. Hawkes: “whistling, crackling noise” (44).
Jeremy Belknap: “like running one’s thumb and forefinger down a silk scarf” (44).
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘Eclippse’ by Radical Face off his album Sunn Moonn Eclippse. Check out the video in the album link, it’s amazing.
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught

Stargazing is a difficult task, especially under adverse weather conditions, but human beings have also made it much harder for ourselves with all these pesky electrical lights and such. Light pollution affects vast swathes of inhabited land, but the introduction of Dark Sky Reserves helps to improve observational conditions for amateur and professional astronomers. Today, you get to hear more about Dark Sky Reserves as well as the Bortle Scale, which is used to judge the amount of light pollution affecting stargazing within an area.
Below the cut are my sources, music credits, a vocab list, and the transcript of this episode. Suggest what you think I should research next by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me. Please subscribe on iTunes, rate it and maybe review it, and tell friends if you think they’d like to hear it!
(My thoughts on the next episode are space race history, the transit of Venus, Shen Kuo, or Walter Baade. The next episode will be up on December 18th.)
Glossary
airglow - a very faint, bluish, naturally occurring glow that hangs around the horizon on Earth, usually within about 15 degrees of the horizon line.
Bortle Scale - an objective scale to measure the clarity and effect of light pollution on a night’s stargazing. Black and grey zones are the best for stargazing, blue is for rural skies, green and yellow are the rural/suburban transition zone, orange is the suburban sky, red is bright suburbia, and white is for cities and inner cities.
deep-sky object - any cosmological object that isn’t individual stars or something from our Solar System. It’s a classification that includes nebulae, galaxies, and star clusters, and it has its roots in amateur astronomy.
ecliptic - the path of the Sun across the sky over the course of a year.
gegenschein - a faint brightening in the night sky directly opposite the Sun. Astronomers think it’s caused by the reflection of sunlight off of dust ejected by comets or resulting from asteroid destruction.
light pollution - the excessive, misdirected, or intrusive use of artificial, human-made lighting. There are several major types of light pollution:
glare - when too-bright and poorly directed lights blind people.
light trespass - when neighboring lights are so bright that their light spills over and illuminates others’ property.
overillumination - when excessive lights are used in a small area.
skyglow - the visible glow caused by light scattering and reflecting off of the droplets of atmospheric molecules.
lumen - a measurement of a light’s brightness.
magnitude - the measurement of a star’s brightness as seen from Earth. The brighter it is, the lower its magnitude value. Ex. the Sun has an apparent magnitude of -27.
Messier object - a deep-sky object included on a list of 103-110 deep-sky objects made by Charles Messier and his colleagues in the 18th century in an attempt to prevent fuzzy, bright objects from being confused with comets.
zodiacal light - a faint brightening in the night sky along the ecliptic that results from sunlight scattered forward off dust in the direction of the Sun.
Transcript
Sources
Sodium lamp light pollution reduction effects via Flagstaff Dark Skies Coalition
Types of light pollution via the British Astronomical Association’s Campaign for Dark Skies, 2009
Light pollution via Sky and Telescope, Dec 2008
The World Atlas of Artificial Night Sky Brightness via the Light Pollution Science and Technology Institute
Lumens and watts via Lowes
UNESCO World Heritage Site list
Invention of the light bulb via SPS Industrial
Lightbulb components via CIO
Walter Baade bio via the Royal Astronomy Society of Canada
International Dark-Sky Association
“An IDA International Dark Sky Reserve is a public or private land possessing an exceptional or distinguished quality of starry nights and nocturnal environment that is specifically protected for its scientific, natural, educational, cultural, heritage and/or public enjoyment. Reserves consist of a core area meeting minimum criteria for sky quality and natural darkness, and a peripheral area that supports dark sky preservation in the core. Reserves are formed through a partnership of multiple land managers who have recognized the value of the natural nighttime environment through regulations and long-term planning.”
“The core area must provide an exceptional dark sky resource, relative to the communities and cities that surround it, where the night sky brightness is routinely equal to or darker than 20 magnitudes per square arc second.”
John Bortle’s article on his magnitude scale via Sky and Telescope, July 2006
“I have created a nine-level scale. It is based on nearly 50 years of observing experience. I hope it will prove both enlightening and useful to observers — though it may stun or even horrify some! Should it come into wide use, it would provide a consistent standard for comparing observations with light pollution.”
John E. Bortle receives the Leslie C. Peltier Award in 2013 via the Astronomical Society
Bortle dark sky scale via Big Sky Astronomy Club
Bortle dark sky scale via LSU
Gegenschein via Sky and Telescope, Oct 2015
Messier List via Fred Espenak’s website, Astropixels
Caldwell List via Students for the Exploration and Development of Space (SEDS)
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘New Son/Burnt Iron’ by Trampled by Turtles off their album Palomino
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught

Spacewalk complete and new astronaut record set! Shane Kimbrough and Peggy Whitson of NASA successfully reconnected cables and electrical connections on an adapter-3 that will provide the pressurized interface between the station and the second of two international docking adapters to be delivered to the complex to support the dockings of U.S. commercial crew spacecraft in the future. The duo were also tasked with installing four thermal protection shields on the Tranquility module of the International Space Station.
Having completed her eighth spacewalk, Whitson now holds the record for the most spacewalks and accumulated time spacewalking by a female astronaut. Spacewalkers have now spent a total of 1,243 hours and 42 minutes outside the station during 199 spacewalks in support of assembly and maintenance of the orbiting laboratory.
Astronaut Thomas Pesquet of ESA posted this image and wrote, ’ Shane and Peggy on their way to their first #spacewalk tasks.’
Credit: ESA/NASA

First Female U.S. Astronaut, Sally Ride, Comes Out In Obituary | BuzzFeed
“I hope it makes it easier for kids growing up gay that they know that another one of their heroes was like them,” Sally Ride’s sister, Bear Ride, said.





Equal opportunity benefits can be far-reaching
https://twitter.com/sarahmei/status/818682610712866817

After spending a month attached to the ISS, the Dragon spacecraft succesfully lands in the pacific and is shipped back to land.
via reddit

An episode late is better than none at all! Hear about satellites, space probes, orbiters, and landers through history.
Below the cut are sources, music credits, an awesome infographic showing all the satellites currently in orbit around Earth, a vocab list, and the transcript of this episode. Let me know what you think I should research next by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me in real life. And please check out the podcast on iTunes, rate it or review it if you’d like, subscribe, and maybe tell your friends about it if you think they’d like to listen!
(My thoughts on the next episode were space race history, the transit of Venus, or maybe something about the Moon landing. I’m prepping to interview a friend about her graduate-level research into the history of the universe and possibly dark matter, too. Let me know by the 8th and I’ll hopefully have the next podcast up on September 18th!)
Glossary
Clarke Belt - an area of geostationary orbit in Earth’s atmosphere, 35,786 km directly above the equator, where a satellite orbits the Earth at the same speed the Earth is rotating.
geostationary orbit - when an object orbits directly above the equator and appears stationary to observers on Earth’s surface.
geosynchronous orbit - when an object orbits Earth at an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis. From the perspective of an observer on Earth's surface, the object would return to the exact same position in the sky after a period of one day.
gyroscopes - a device consisting of several rings that spin freely around different axes. The rapidly rotating wheel has a large moment of inertia and therefore resists change from the plane in which it is rotated. Large gyroscopes allow for steady navigation of ships, submarines, and space ships. See examples in the link.
heliosheath - the outer region of the heliosphere. It is just beyond termination shock, the point where solar wind abruptly slows down and becomes denser and hotter as it presses outward against the approaching wind in interstellar space.
heliosphere - a huge wind sock-shaped bubble that extends beyond Pluto’s orbit and contains our solar system, solar wind, and the entire solar magnetic field.
lander - a spacecraft launched with the intent to land it, unharmed and fully functioning, on the surface of an object that is astronomical in nature. It is aimed at a specific target that astronomers want to learn more about and investigates the object at the surface level. It can be manned or unmanned.
orbiter - an unmanned spacecraft launched with the intent to bring it into orbit around a larger body in order to study that body. It is similar to a satellite but does not orbit Earth.
probe - an unmanned machine sent into space to collect data. It is aimed at a specific target that astronomers want to learn more about.
spacecraft - a pilot-able vehicle used for traveling in space. It can be manned or unmanned.
Van Allen Belts - belts of radiation in Earth’s atmosphere.
Transcript
Sources
Timeline of space exploration to 2013 via the National Archives
Timeline of NASA, the space shuttle, and near-Earth space flights
Space exploration timeline via Sea and Sky
Gyroscope definition via USC
Infographic on satellites launched 1950-1978 via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
List of satellites via Wikipedia
A history of Sputnik via an excerpt from Paul Dickson’s book Sputnik: The Shock of the Century on PBS
“Instead of being concerned with winning the first round of the space race, Eisenhower and his National Security Council were much more interested in launching surveillance satellites that could tell American intelligence where every Soviet missile was located.”
Explorer 1 overview via NASA
Vanguard 1 overview via NASA
SCORE overview via the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum
Pioneer lunar mission overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Various probe/satellite mission overviews via NASA
Australian WRESAT mission via Australia’s Department of Defence
Pioneer expeditions via NASA
Mariner 10 mission overview via NASA
Magellan mission overview via NASA
Synthetic aperture radar overview via radartutorial.edu
MESSENGER mission overview via JHU Applied Physics Lab
Mariner missions to Venus overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Mariner missions to Mars overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
“The final Mariner to Mars, however, was the lab’s greatest planetary success to date.”
Mariner 9 via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Viking mission overview via NASA
Pathfinder/Sojourner mission overview via NASA
Opportunity mission overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Spirit mission overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Curiosity rover via NASA
Pioneer 10 mission overview via NASA
Pioneer 11 mission overview via NASA
Juno mission overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Cassini-Huygens mission overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Voyager mission overview via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
“The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth.”
Voyager mission trackers via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Heliosphere definition via NASA
Heliosheath definition via NASA
New Horizons mission overview via NASA
Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory via NASA
Chandra X-Ray Observatory via NASA
Spitzer Space Telescope via CalTech
Einstein Observatory (HEAO-2) via NASA
International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) via NASA
International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) via ESA
Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer (EUVE) via NASA
Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics (ASCA, formerly ASTRO-D) via NASA archives
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) via JHU
Active space probe/observatory missions via NASA
Chandrayaan-1 via the CalTech Jet Propulsion Lab
Hayabusa 2 mission overview via NASA
Hayabusa-2’s twitter account
A map of every active satellite orbiting Earth via Quartz
Union of Concerned Scientists Satellite Database
Cul-de-Sac comic by Richard Thompson
“Well, there’s dust everywhere, and there’s all kinds of trash—food wrappers and broken parts of things and gloves and shoes. And gas giants and black holes and rocks and dirt. And there’s old TV shows and strange creatures and there’s unidentifiable stuff that no one can explain. And it’s expanding all the time. Toss in a few trillion stuffed toys and it’d be just like your room.”
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘Satellite’ by Guster off their album Ganging Up On The Sun
Filler Music: ‘Sunn’ by Radical Face off his album Sunn Moonn Eclippse. Check out the video in the album link, it’s amazing.
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught.
How does a microgravity garden grow when there’s no up or down? An advanced chamber, about the size of a mini-fridge, is giving us a clearer perspective of plant growth habits. Without gravity and the addition of a wide variety of light and humidity settings, the plants cultivated on the International Space Station provide a world of opportunity to study space-based agricultural cycles.
Learn more about our space garden HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

In November, a couple lovely people brought my attention to articles about a recent discovery that headlines consistently referred to as the ‘zombie star.’ What the heck is a zombie star? What makes it a zombie? I found a zombie star from 2014 in addition to the one in 2017 and I dug into the life cycle of the average star to get a sense of what undeath looks like in stars.
Below the cut are my sources, music credits, a vocab list, and the transcript of this episode. Suggest what you think I should research next by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me. Please subscribe on iTunes, rate it and maybe review it, and tell friends if you think they’d like to hear it! Also, welcome if you found me through PodCon!
(My thoughts on the next episode are the International Space Station, the transit of Venus, or astronaut training practices. The next episode will allegedly be up on New Year’s Day, January 1st. We’ll see about that.)
Glossary
Chandrasekhar limit - the upper limit for the mass of an astronomical body that can support extreme density without imploding: about 1.4 times the mass of our Sun. Any white dwarf star that has less than that mass will stay a white dwarf forever; any star that exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit will end in a supernova.
dwarf nova - a close binary system of a red dwarf, a white dwarf, and an accretion disk around the white dwarf. They brighten by 2 to 6 magnitudes depending on the stability of the disk, which loses material to the white dwarf. Categorized as a cataclysmic variable.
neutron star - a type of star that has gone supernova, when the surviving core is 1.5 to 3 solar masses and contracts into a small, very dense, very fast-spinning star.
nova - a close binary system of a white dwarf and a secondary star that’s a little cooler than the Sun. The system brightens 7 to 16 magnitudes in 1 to 100 days, and then the star fades slowly to the initial brightness over a period of several years or decades. At maximum brightness, it’s similar to an A or F giant star. Recurrent novae are similar to this category of variable but have several outbursts during their recorded history. Categorized as a cataclysmic variable.
pulsar - a type of neutron star that spins very, very fast. Also a kind of variable star that emits light pulses usually between 0.0014 seconds and 8.5 seconds.
reflection telescope - reflects light rays off the concave surface of a parabolic mirror to get an image of a distant object. Higher contrast image, worse color quality.
spectroscopy - the study of light from an incandescent source (or, more recently, electromagnetic radiation and other radiative energy) that has its wavelength dispersed by a prism or other spectroscopic device that can disperse an object’s wavelength. The spectra of distant astronomical objects like the Sun, stars, or nebulae are patterns of absorption lines that correspond to elements that these objects are made up of.
supernova - a massive star that explodes with a magnitude increase of 20 or more. Supernovae have led us to realize that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating.
supernova progenitors - the kinds of stars and conditions that will result in certain types of supernovae.
white dwarf star - a star that has exhausted all of its nuclear fuel (i.e. no longer has hydrogen to convert into helium through nuclear fusion). It is the hot, dense core of a star. Unless it is acquiring/accreting matter from a nearby star, it will cool over time and become a dead star.
Script/Transcript
Sources
Chandrasekhar limit via PBS, Jan 2012
“The Chandrasekhar Limit is therefore not just as upper limit to the maximum mass of an ideal white dwarf, but also a threshold. A star surpassing this threshold no longer hoards its precious cargo of heavy elements. Instead, it delivers them to the universe at large in a supernova that marks its own death but makes it possible for living beings to exist.”
Type I and Type II supernovae via Space.com
Type Ia supernovae via Swinburne University of Technology
Type Ia Supernova Progenitors via Swinburne University of Technology
Zombie star via NASA, Aug 2014
Curtis McCully “I was very surprised to see anything at the location of the supernova. We expected the progenitor system would be too faint to see, like in previous searches for normal Type Ia supernova progenitors. It is exciting when nature surprises us.”
The abstract of the article McCully and his team wrote on Type 1ax supernovae via Nature Magazine, Aug 2014
Zombie star via CNN, Nov 2017
Arcavi: "My first thought was that this must be some nearby star in our galaxy, just varying its brightness. But when we got the first spectrum of it, we saw that it was in fact a supernova 500 million light-years away. My mind was blown. The fact that it got bright and dim five times was very unusual. We'd never seen a supernova do that before."
Arcavi: "This means that we still have a lot to learn about how massive stars evolve and how they explode."
Robert Evans via Sky and Telescope, Sept 2005
2017 zombie star articles I didn’t use because there were too many of them:
Air and Space Magazine, Nov 2017
The Atlantic, Nov 2017
BBC News, Nov 2017
BGR, Nov 2017
Carnegie Science, Nov 2017
Earth Sky, Nov 2017
Express UK, Nov 2017
The Guardian, Nov 2017
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: 'Toll Free’ by the Shook Twins off their album What We Do
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught
-
 now-you-no reblogged this · 4 years ago
now-you-no reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 1978mikhail liked this · 7 years ago
1978mikhail liked this · 7 years ago -
 mojomatao reblogged this · 7 years ago
mojomatao reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 usuallyinstantruins liked this · 7 years ago
usuallyinstantruins liked this · 7 years ago -
 illume77 reblogged this · 8 years ago
illume77 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 stiuvar-elnor reblogged this · 8 years ago
stiuvar-elnor reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 deception1 reblogged this · 8 years ago
deception1 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 fluseicsspacechaos reblogged this · 8 years ago
fluseicsspacechaos reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 miller-bot reblogged this · 8 years ago
miller-bot reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 imthebeholder reblogged this · 8 years ago
imthebeholder reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tvnacity reblogged this · 8 years ago
tvnacity reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 flyingunderstars reblogged this · 8 years ago
flyingunderstars reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dsnoopyzi-blog liked this · 8 years ago
dsnoopyzi-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 dsnoopyzi-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
dsnoopyzi-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 talkativetiad reblogged this · 8 years ago
talkativetiad reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thalasa101 reblogged this · 8 years ago
thalasa101 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thalasa101 liked this · 8 years ago
thalasa101 liked this · 8 years ago -
 inactivepennnybites liked this · 8 years ago
inactivepennnybites liked this · 8 years ago -
 mariah-banks reblogged this · 8 years ago
mariah-banks reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 clairvoyant-fry-cook liked this · 8 years ago
clairvoyant-fry-cook liked this · 8 years ago -
 eldritch-sanctum liked this · 8 years ago
eldritch-sanctum liked this · 8 years ago -
 cottonasphalt liked this · 8 years ago
cottonasphalt liked this · 8 years ago -
 gossamerskulls-blog liked this · 8 years ago
gossamerskulls-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 jamven liked this · 8 years ago
jamven liked this · 8 years ago -
 dragonsoul liked this · 8 years ago
dragonsoul liked this · 8 years ago -
 arcanisthenotsoomnipotent liked this · 8 years ago
arcanisthenotsoomnipotent liked this · 8 years ago -
 ftagn reblogged this · 8 years ago
ftagn reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ftagn liked this · 8 years ago
ftagn liked this · 8 years ago -
 burn-oxygen-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
burn-oxygen-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 burn-oxygen-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
burn-oxygen-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 venezzy reblogged this · 8 years ago
venezzy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 oddlittlespaceace reblogged this · 8 years ago
oddlittlespaceace reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 hellamellokitty-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
hellamellokitty-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gnnttkc reblogged this · 8 years ago
gnnttkc reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 bruised-scarred-broken reblogged this · 8 years ago
bruised-scarred-broken reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 bruised-scarred-broken liked this · 8 years ago
bruised-scarred-broken liked this · 8 years ago -
 inconspicuous-things reblogged this · 8 years ago
inconspicuous-things reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 trippypeas reblogged this · 8 years ago
trippypeas reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ca00-blog liked this · 8 years ago
ca00-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 steviegskillz reblogged this · 8 years ago
steviegskillz reblogged this · 8 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts