Heya, If You Like Space Maybe You’ll Like This Comic? It’s One Of My Favorites And It’s Ending
Heya, if you like space maybe you’ll like this comic? It’s one of my favorites and it’s ending soon and it’s all online for freebies! The spaceships are fish and folks get to go around fixing up abandoned ruins in space. It’s utterly beautiful. It’s also ending this month!









We’ll make it out eventually.
http://www.onasunbeam.com/
(New chapters coming soon)
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others

Haaaaaay I’m on iTunes now! Slightly more convenient to download maybe!

A teenager designed a pocket-sized satellite that will fly on a NASA mission
An 18-year-old created the world’s lightest functioning satellite, and it’s going to be launched on a real NASA mission next month.
Rifath Sharook, who is from Tamil Nadu, India, made the pocket-sized satellite for a competition called Cubes in Space, which is an international design challenge that asks students aged 11 to 18 to fit their space-worthy invention inside a 13-foot cube.
The pocket-sized 3-D printed satellite is much smaller than that. It weighs just 0.14 pounds and will measure the rotation, acceleration and magnetosphere of Earth, Sharook told Business Standard. Read more (5/17/17)
follow @the-future-now
Voyager is so happy, because it’s the bravest satellite of all. It has gone the furthest. And it’s not lonely, because it’s talking to us. It phones home. And it tells us all about the wonderful things that it’s seeing. …There’s a whole universe to explore, and it’s just leaving our Solar System right now. It’s very brave and very lucky to be doing what it’s doing, so it’s not going to get lost. It’s traveled further than anything we’ve ever built has traveled before. It’s actually showing us the way. … It might have been safer for it to just stay home, and stay inside a building, but then it would have been sad forever, because it never would have done its purpose. It never would have discovered things. It’s all a wonderful story of great discovery and success, and it couldn’t have happened if Voyager hadn’t been brave… It’s not really the fact that everything always has a start and an end, it’s what happens in the middle that counts. What do you while you’re alive? What do you do while you’re laughing? And I think we’re doing exactly what makes Voyager joyful and as happy as it could be. Think about the fact that you’re a little bit like Voyager. In that you’re going to go see the world, and you’re going to call your mom on the phone and tell her about the wonderful things that you see. … You wouldn’t want to spend your whole life hiding under your bed and never seeing anything in your whole life, you want to be able to do what makes you happy and joyful and learn about things to discover. You might be the person that discovers something really important for everybody else on the world, but you can never discover that if you just hide and only do things that are safe. So think about yourself a little bit like Voyager. What makes you laugh? It’s not just staying, hiding underneath your bed safely at home.
Cmdr. Chris Hadfield, reassuring a five-year-old who was worried about the Voyager satellite (source)
oh no I’m having feelings about a satellite
tagging Doctor Who, because.
(via reconditarmonia)

The process of making an audio and visual compilation to explain Earth and humanity to an alien species is an incredible undertaking, and Carl Sagan undertook it in 1977. The resulting record from his little team was sent out with the Voyager 1 and 2 probes and is now in interstellar space, but there was also a more personal result of this project. Learn about Sagan and his third wife’s meet-cute and also hear what is actually out there in the stars, conveying the best humanity had to offer in the 70s.
Below the cut are my sources, music credits, a vocab list, and the transcript of this episode. Vote on what you think I should research next by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me in real life. And please subscribe to the podcast on iTunes, rate it and maybe review it, and tell friends if you think they’d like to listen!
(My thoughts on the next episode are space race history, the transit of Venus, Edmond Halley, or Dark Sky Preserves. Next episode will be up on December 4th.)
Glossary
electroencephalography (EEG) - a recording that displays brainwave activity by measuring the electrical impulses of neurons firing in the brain
heliosheath - the outer region of the heliosphere. It is just beyond termination shock, the point where solar wind abruptly slows down and becomes denser and hotter as it presses outward against the approaching wind in interstellar space.
heliosphere - a huge wind sock-shaped bubble that extends beyond Pluto’s orbit and contains our solar system, solar wind, and the entire solar magnetic field.
Transcript
Sources
Drunk History episode transcript
Golden record via NASA
Carl Sagan via Smithsonian Magazine, March 2014
Carl Sagan via Biography.com
Carl Sagan via National Geographic
The Voyager project love story via NASA
Ann Druyen: “We know that EEG patterns register some changes in thought. Would it be possible, I wondered, for a highly advanced technology of several million years from now to actually decipher human thoughts?"
Ann Druyen: "a mental itinerary of the ideas and individuals of history whose memory I hoped to perpetuate."
Ann Druyen: "My feelings as a 27-year-old woman, madly fallen in love, they're on that record. It's forever. It'll be true 100 million years from now. For me, Voyager is a kind of joy so powerful, it robs you of your fear of death."
Arthur C. Clarke: "Please leave me alone; let me go on to the stars."
How 8-track tapes work via 8 Track Heaven
How vinyl records work via The Guardian, June 2010
Golden record via Smithsonian Magazine, April 2012
Golden record via the JPL at NASA
Golden record retrospective by Timothy Ferris via The New Yorker, August 2017
Voyager Golden Record - Greetings In 55 Languages via YouTube
The 116 images NASA wants aliens to see via YouTube
The Voyagers documentary by Penny Lane via Brain Pickings
Ann Druyen: “Carl and I knew we were the beneficiaries of chance, that pure chance could be so kind that we could find one another in the vastness of space and the immensity of time. We knew that every moment should be cherished as the precious and unlikely coincidence that it was.”
Article on Sagan’s divorce from Linda Salzman Sagan via People, December 1980
Article on Sagan’s divorce from Linda Salzman Sagan via The Cornell Daily Sun, March 1981
Voyager record available on Soundcloud via Cosmos Magazine
Golden record now available for purchase via The Atlantic, August 2017
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘Dark Was The Night, Cold Was The Ground’ by Blind Willie Johnson (1897-1945) off the album Dark Was The Night ‘Carl Sagan’ by Loch Lomond off their album Paper The Walls
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught

After over a century of observations and several theories, scientists may have finally nailed the origin of the high-speed plasma blasting through the Sun’s atmosphere several times a day. Using a state-of-the-art computer simulation, researchers have developed a detailed model of these plasma jets, called spicules.
The new findings answer some of the bigger questions in solar physics, including how these plasma jets form and why the Sun’s outer atmosphere is far hotter than the surface.
“This is the first model that has been able to reproduce all the features observed in spicules,” Juan Martinez-Sykora, lead author and astrophysicist at the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute in California, told ScienceAlert.
Continue Reading.
Here’s a great example of the kinds of experiments astronauts perform on the International Space Station, just like I talked about in Episode 19! I absolutely want to high-five whoever called is ISS-CREAM.
From Frozen Antarctica to the Cold Vacuum of Space
A new experiment that will collect tiny charged particles known as galactic cosmic rays will soon be added to the International Space Station. The Cosmic Ray Energetics And Mass for the International Space Station payload, nicknamed ISS-CREAM, will soon be installed in its new home on the Station’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility. ISS-CREAM will help scientists understand more about galactic cosmic rays and the processes that produce them.

Wait, what are cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are pieces of atoms that move through space at nearly the speed of light. Galactic cosmic rays come from beyond our solar system.

They provide us with direct samples of matter from distant places in our galaxy.
Why do these things go so fast?
Galactic cosmic rays have been sped up by extreme processes. When massive stars die, they explode as supernovas. The explosion’s blast wave expands into space along with a cloud of debris.

Particles caught up in this blast wave can bounce around in it and slowly pick up speed. Eventually they move so fast they can escape the blast wave and race away as a cosmic ray.
Where can we catch cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are constantly zipping through space at these super-fast speeds, running into whatever is in their path – including Earth.

But Earth’s atmosphere is a great shield, protecting us from 99.9 percent of the radiation coming from space, including most cosmic rays. This is good news for life on Earth, but bad news for scientists studying cosmic rays.
So… how do you deal with that?
Because Earth has such an effective shield against cosmic rays, the best place for scientists to study them is above our atmosphere – in space. Since the 1920s, scientists have tried to get their instruments as close to space as possible. One of the simplest ways to do this is to send these instruments up on balloons the size of football stadiums. These balloons are so large because they have to be able to both lift their own weight and that of their cargo, which can be heavier than a car. Scientific balloons fly to 120,000 feet or more above the ground – that’s at least three times higher than you might fly in a commercial airplane!

Credit: Isaac Mognet (Pennsylvania State University)
Earlier versions of ISS-CREAM’s instruments were launched on these giant balloons from McMurdo Station in Antarctica seven times, starting in 2004, for a total of 191 days near the top of the atmosphere. Each of these flights helped the team test their hardware and work towards sending a cutting-edge cosmic ray detector into space!
How is going to space different than flying balloons?
Balloon flights allowed the team to collect a lot of cosmic rays, but even at 120,000 feet, a lot of the particles are still blocked. Scientists at the University of Maryland, College Park, who operate ISS-CREAM, expect to get about 10 times as much data from their new home on the International Space Station.

That’s because it will be both above the atmosphere and fly far longer than is possible with a balloon. As you might imagine, there are large differences between flying something on a balloon and launching it into space. The science instruments and other systems had to be changed so ISS-CREAM could safely launch on a rocket and work in space.
What will ISS-CREAM do?
While on the space station, ISS-CREAM will collect millions of cosmic rays – electrons, protons and atomic nuclei representing the elements found in the solar system. These results will help us understand why cosmic rays reach the wicked-fast speeds they do and, most important, what limits those speeds.
ISS-CREAM launches to the International Space Station aboard the latest SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, targeted to launch August 14. Want to learn more about ISS-CREAM and some of our scientific balloons? Check out our recent feature, NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program Reaches New Heights.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
I'm reading Starlight Detectives pretty hard cuz new episode goes up on Monday and let me tell you, I now have a very deep appreciation for the photographs we have of space.

Small Magellanic Cloud: Stunning Infrared Image
For the love of all that’s good and proper click here and zoom way into this image. It’s more than beautiful. The fact that it’s infrared means that we’re able to see past a lot of the dust that would otherwise block our view.
(Image credit: ESA/VISTA)
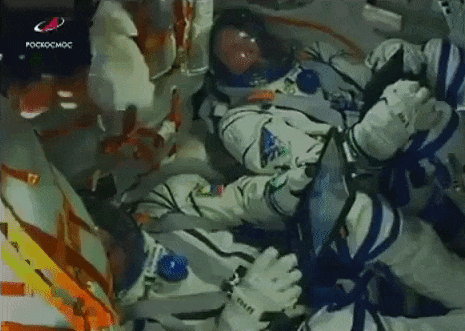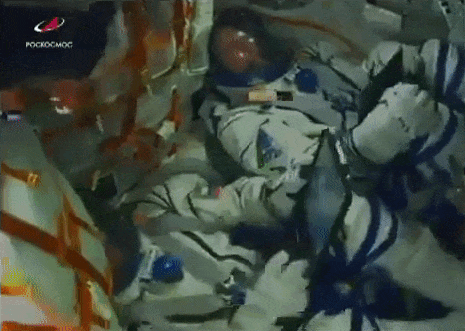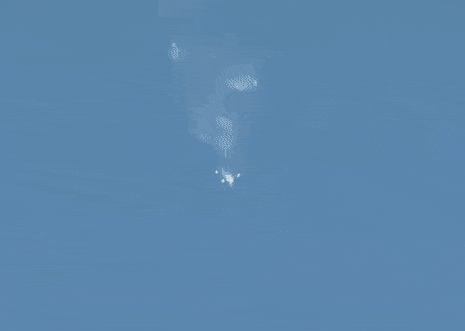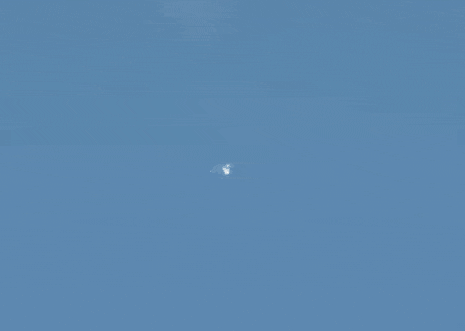
Soyuz MS-10 experiences launch anomaly; crew aborts to safe landing.
One of Russia’s most reliable launchers experienced a rare, in-flight anomaly earlier this morning, forcing the two-man crew of Soyuz MS-10 to abort the mission.
Following a normal liftoff at 4:40am EST (2:40pm local time), a malfunction in the Soyuz FG rocket two minutes into the flight forced Expedition 57 crewmembers Alexey Ovchinin and Nick Hague to abort a manual abort profile. The anomaly occurred immediately following the separation of the rocket’s four strap-on boosters and jettisoning of the Launch Escape System. However, the protective fairing covering the spacecraft during flight through the thick atmosphere was still on, and solid rocket motors attached to the fairing pulled the crew capsule away from the failing booster. Following a ballistic trajectory through the upper atmosphere, the Soyuz’s Descent module separated from the Orbital Module and payload fairing and descended to a safe landing 20 kilometers east of Zezkezhan, Kazakhstan, 34 minutes after launch. Roscosmos reported that the crewmembers experienced around seven times the force of gravity, or 7G’s, during their abort.
Recovery forces reached the landing site immediately following touchdown. Both astronauts were reported to be in good health following their ordeal, and returned to their families at the Baikonur launch site around six hours after liftoff.

Recovery forces at the Soyuz MS-10 emergency landing site. Source: Ruptly.

Soyuz MS-10 crewmembers Alexey Ovchinin and Nick Hague embrace their families following their return to the Baikonur Cosmodrome after today’s launch mishap. Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls. This marks the first crewed launch mishap of the International Space Station program, the first crewed launch mishap since the Challenger disaster in 1986, and the first crewed Soyuz launch malfunction since Soyuz T-10 in 1983.
That incident saw the two-man crew of Vladimir Titov and Gennady Strekalov abort away from their exploding rocket shortly before its scheduled liftoff time. While no cause of the mishap is currently known, Russian authorities have begun an investigation of the incident and have temporarily grounded all future Soyuz flights. The current three-member crew of Expedition 57 is slated to return to Earth December 13, followed by the launch of Expedition 58 December 20. Following today’s anomaly, it is unclear whether Expedition 57 will remain on orbit longer, or when the next crew will launch to the station. Expedition 57 is able to remain on orbit until early January, when their Soyuz reaches its certified orbital lifetime.

Expedition 57 commander Alexander Gerst captured this image of the Soyuz MS-10 launch from the International Space Station. The anomalous nature of the launch is evidenced by multiple points of light along the ascent path. Source: NASA. Watch NASA TV coverage of the Soyuz MS-10 launch below.
P/c: NASA.

TODAY IN HISTORY: The first-ever color image of Mars, taken by NASA’s Viking 1 lander on July 21, 1976. (San Diego Air & Space Museum)
-
 soidokno liked this · 3 years ago
soidokno liked this · 3 years ago -
 azako liked this · 4 years ago
azako liked this · 4 years ago -
 hues-of-purple liked this · 5 years ago
hues-of-purple liked this · 5 years ago -
 liapher reblogged this · 5 years ago
liapher reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 chthonicmoons reblogged this · 6 years ago
chthonicmoons reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 gh0stposting liked this · 6 years ago
gh0stposting liked this · 6 years ago -
 rllycloudstar liked this · 6 years ago
rllycloudstar liked this · 6 years ago -
 disgruntled-insomniac liked this · 6 years ago
disgruntled-insomniac liked this · 6 years ago -
 gracebriarwoodwrites liked this · 6 years ago
gracebriarwoodwrites liked this · 6 years ago -
 bubilee reblogged this · 7 years ago
bubilee reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 bubilee liked this · 7 years ago
bubilee liked this · 7 years ago -
 little-sputik reblogged this · 7 years ago
little-sputik reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 flourescent-bubbles liked this · 7 years ago
flourescent-bubbles liked this · 7 years ago -
 michaelrodz liked this · 7 years ago
michaelrodz liked this · 7 years ago -
 danishinsp reblogged this · 7 years ago
danishinsp reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 santiagoreds liked this · 7 years ago
santiagoreds liked this · 7 years ago -
 fly-don liked this · 7 years ago
fly-don liked this · 7 years ago -
 a-melioratio-n liked this · 7 years ago
a-melioratio-n liked this · 7 years ago -
 xdrikal liked this · 7 years ago
xdrikal liked this · 7 years ago -
 vflores4-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago
vflores4-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 starshinecity reblogged this · 7 years ago
starshinecity reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 badbellamy liked this · 7 years ago
badbellamy liked this · 7 years ago -
 1emwolfilie reblogged this · 7 years ago
1emwolfilie reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thewindowofthesummerhouse liked this · 7 years ago
thewindowofthesummerhouse liked this · 7 years ago -
 ugetwhatuget liked this · 7 years ago
ugetwhatuget liked this · 7 years ago -
 pigpenspen reblogged this · 7 years ago
pigpenspen reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 pinastri4 liked this · 7 years ago
pinastri4 liked this · 7 years ago -
 tamed-foxes reblogged this · 7 years ago
tamed-foxes reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 abnerrollins liked this · 7 years ago
abnerrollins liked this · 7 years ago -
 gummmy liked this · 7 years ago
gummmy liked this · 7 years ago -
 stick-arms liked this · 7 years ago
stick-arms liked this · 7 years ago -
 nachoa liked this · 7 years ago
nachoa liked this · 7 years ago -
 greasysweetness liked this · 7 years ago
greasysweetness liked this · 7 years ago -
 justaddspace liked this · 7 years ago
justaddspace liked this · 7 years ago -
 brandonzuckerman liked this · 7 years ago
brandonzuckerman liked this · 7 years ago -
 mendelpalace reblogged this · 7 years ago
mendelpalace reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 blueheartedgal liked this · 7 years ago
blueheartedgal liked this · 7 years ago -
 personinthehat liked this · 7 years ago
personinthehat liked this · 7 years ago -
 lifeislove1000 liked this · 7 years ago
lifeislove1000 liked this · 7 years ago -
 tellfires liked this · 7 years ago
tellfires liked this · 7 years ago -
 imaginative-title reblogged this · 7 years ago
imaginative-title reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 houseriot reblogged this · 7 years ago
houseriot reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 scatterbone liked this · 7 years ago
scatterbone liked this · 7 years ago -
 wickedwix reblogged this · 7 years ago
wickedwix reblogged this · 7 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts
